The finished lamb price appears to be stabilising following its seasonal decline. It never reached the highs of last year, but has been trading near or above the five-year average for most of the year. Due to good pasture growth, lambs have been finishing much faster this year and together with a smaller lamb crop, numbers available in the 4th Quarter are expected to be less this year than last. Normally this would bode well for farmgate prices but this year Brexit uncertainty is overshadowing price prospects.
Reports suggest early sheep breeding and store lamb sales have actually seen a good start. This is probably due to good grass growth keeping feeding costs down. Furthermore, the fall in the value of the Pound against the Euro, means that in the short term exports will be competitive. This could even lead to EU countries stock piling UK lamb meat ahead of 31st October; however, this could be met with producers off-loading stock ahead of the Brexit date.
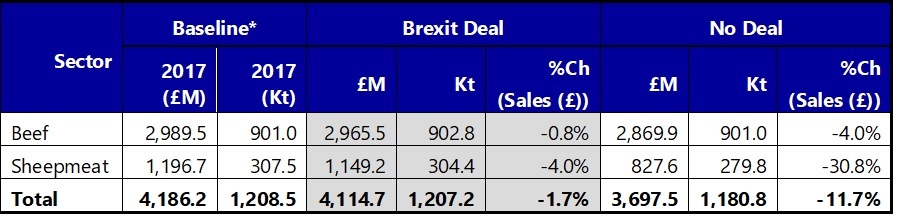
For those with store lambs to sell and those thinking about buying lambs to finish, it is a very difficult decision to make. If we leave the EU with a ‘deal’ on 31st October, this could see us enter into a ‘transition’ period and our current trading arrangements would continue whilst a long term trading position was drawn-up and it would therefore be business as usual. This could mean strong prices because of the reasons cited in the first paragraph above. But leaving the EU without a deal, would see us trading as a third country with the EU under WTO rules, meaning sheep meat exported to the EU market would be subject to significant tariffs and would not be competitive.
Currently, we export about a third of our lamb production and nearly 100% goes to the EU. Losing this market would hit domestic farmgate prices hard. There has been some talk of the EU not imposing such tariffs on us, but this is not possible under WTO rules. Without a Comprehensive Free Trade Agreement, under the ‘most favoured nation’ rule, any changes to the EU tariff would have to be made available to all other countries. In a further twist, New Zealand lamb will still be available tariff free to both the UK and EU due to their tariff rate quotas (TRQs) which are expected to split (50:50) between the EU and UK on our departure.
Of course, there is the possibility of trading with non-EU countries, the global market for sheepmeat is currently pretty strong, due to African Swine Fever in China and less lamb production in both New Zealand and Australia. However, this will take time to develop and is not always that straightforward due to varying regulatory standards, tariffs and the like. The expanding Asian market is the most obvious market opportunity, but the Chinese market is complex. New Zealand already has a FTA with China and have relatively well-established processing partnerships in this market, all of which take time to build.
On balance, for the lamb sector, it is clear that having a Brexit Deal agreed with the EU would be much more favourable than a No Deal which would have major negative repercussions for the sheepmeat industry.